- STEPS
- Finding a system definition
- Characterisation of direct risk
- Characterisation of indirect risk
- Evaluation of direct and indirect risk
- Defining risk management options
- Accounting for future system rate
Risk-Informed Decision-Making
SUMMARY
- The development of a generic, flexible approach to collaborative systems analysis.
- The elaboration of the MYRIAD-EU Framework for individual, multi-, and systematic risk analysis with multiple iterations and additional steps to guide the formulation of Multi-Risk Pathways to address long-term DRR challenges. We refer to this approach as Dynamic Adaptive Policy Pathways for Multi-Risk (DAPP-MR).
- The development of a Storyline approach to qualitatively implement systems and risk analyses and pathways formulation through exploration of both past- and potential future multi-risk events.
Further information on the last two activities can be found on the above linked-to dedicated pages. The remainder of this page concerns the collaborative systems analysis approach.
Collaborative
Systems Analysis
- Avoid negative consequences when approaching problems through a sector-specific lens.
- Aid in the formulation of system-wide objectives that both recognize and balance the inherent trade-offs within systems
- Ensure a more equitable distribution of system-wide resources, costs, and benefits.
- Help reduce the potential for stakeholder conflict.
Our generic approach both supports the development of Multi-Risk Pathways according to the three stages of DAPP-MR and offers a means by which to help users step through the MYRIAD-EU Framework.
- To represent holistic, integrated systems and their key functions, risks, and opportunities.
- To highlight the key interdependencies and interactions between system components, including all feedbacks, trade-offs, and synergies.
- To generate a common, shared understanding of integrated systems and planning objectives among stakeholders.
- To prioritise key system functions, objectives, constraints, risks, and opportunities for the purposes of DRM planning.
- To be flexible to the needs of practitioners and allow for the incorporation of various supporting tools and approaches with which they are comfortable.
The proposed approach consists of three iterative steps. Like DAPP-MR, these gradually increase the degree of system complexity being considered in each step:
- Define system boundaries and constraints
- Undertake sector-based analyses
- Synthesise sector-based analyses into a whole-of-system analysis
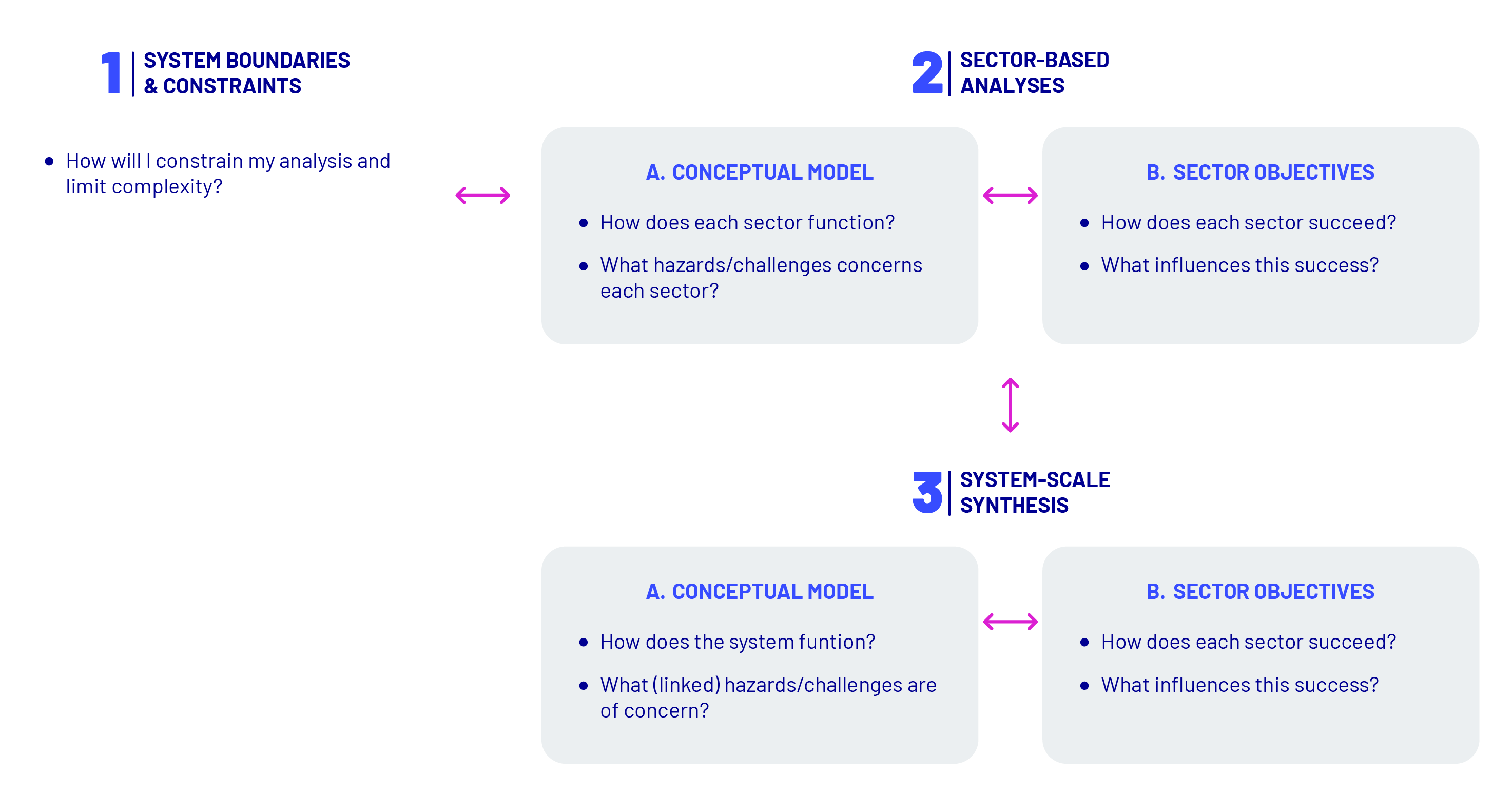
Each step within the approach suggests a list of question prompts to guide practitioners, along with possible participatory methods and tools to be applied to help answer these. Highlighted tools include the DPSIR framework for analysing causal relationships, Causal Loop Diagrams for visualising system causalities, and CIrcle and Interaction Matrices for exploring system interactions. Practitioners should feel free to adapt these as needed to suit their particular problem context and prior experience. Further information on the approach can be found here.
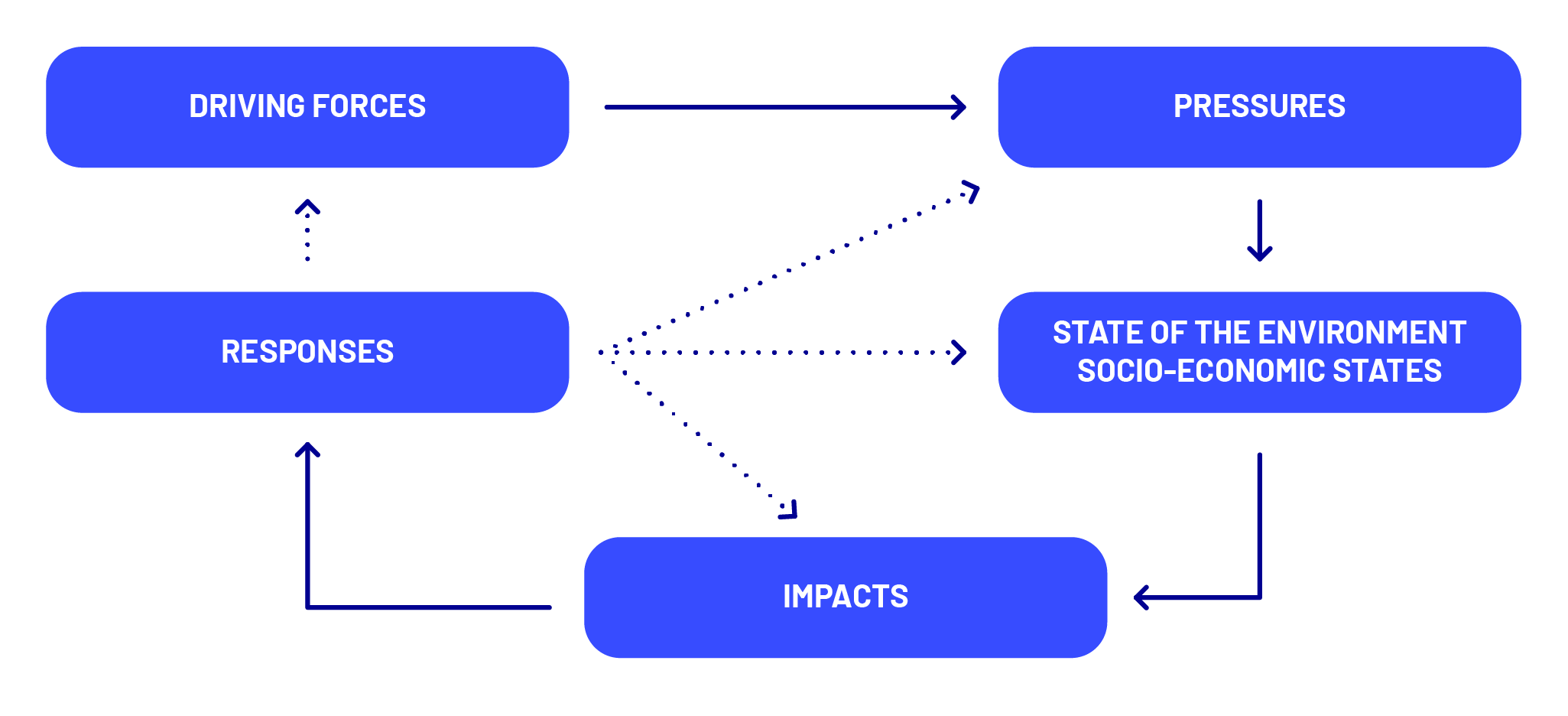
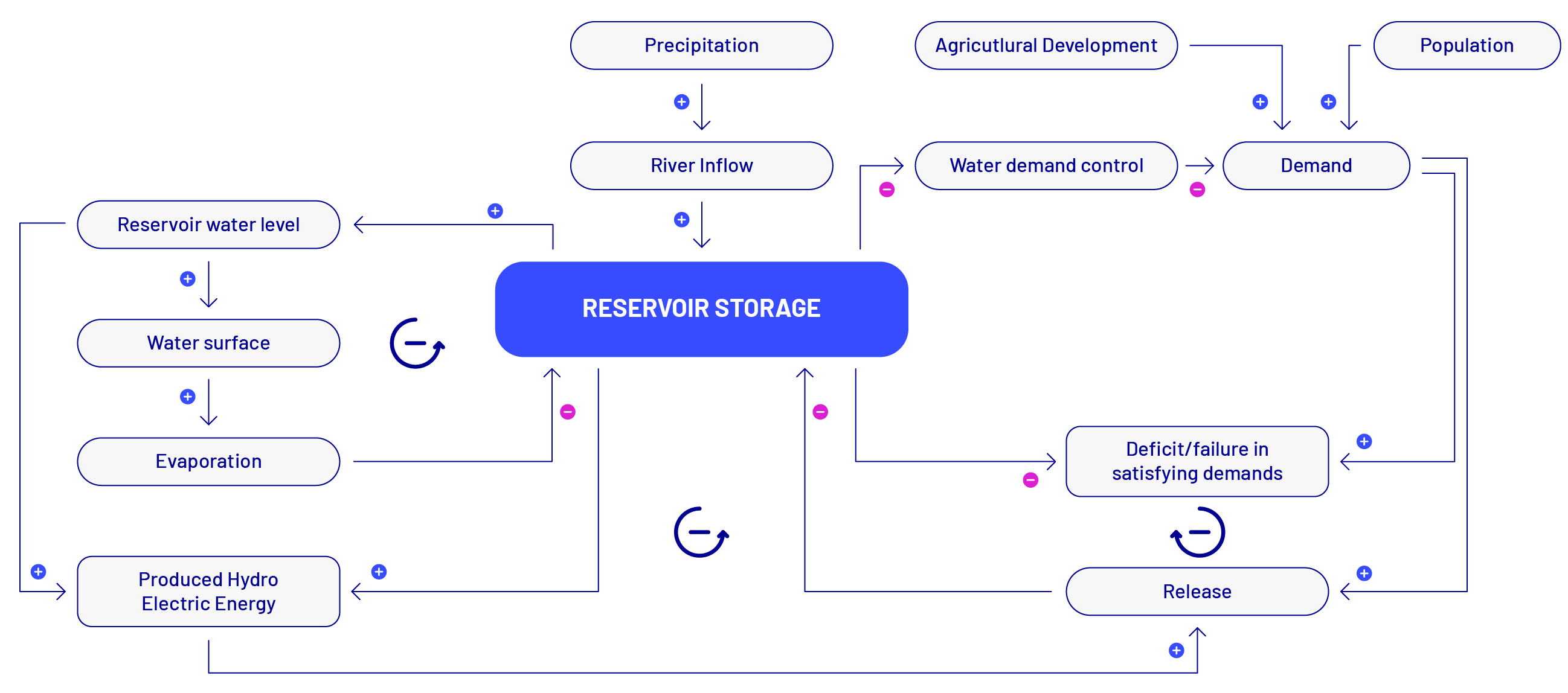
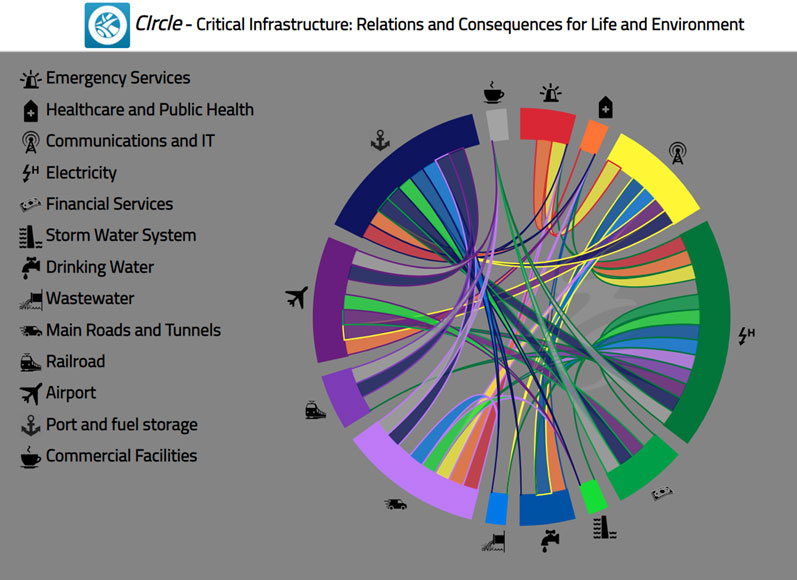
Application of collaborative systems analysis approach with the MYRIAD-EU Framework
The proposed collaborative systems analysis approach complements the MYRIAD-EU Framework insofar as it proposes a means by which to collaboratively undertake the initial framing and context setting aspects of each step in the framework together with stakeholders. The table below summarises the aspects of the framework the proposed approach supports.
Activities in the MYRIAD-EU framework covered by the proposed collaborative systems analysis approach
Finding a system definition
- Identifying the system at hand, its components and clear system boundaries
- Determining the hazards threatening the system and the system’s exposed and vulnerable elements
- Characterising the governance landscape, sustainability challenges, desired vision and initial risk management options for the system
Characterisation of direct risk
- Identifying direct risks resulting from physical contact with the single- or multi-hazard
- Defining direct risk metrics
- Characterising direct risk metrics (i.e., assessing the risks)
Characterisation of indirect risk
- Identifying indirect risks due to interdependencies in the systems
- Defining indirect risk metrics
- Characterising indirect risk metrics (i.e., assessing the risks)
Evaluation of direct and indirect risk
- Defining direct and indirect risk evaluation criteria
- Conducting the evaluation
- Selecting direct and indirect risks to manage
Defining risk management options
- Identifying initial risk management options for the system
- Assessing and evaluating risk management options
- Selecting risk management options for inclusion in the adaptive DRM strategy
Accounting for future system state
- Identifying the key factors driving risk in future system states (e.g., due to processes such as climate change, economic change, land-use change, etc.)
- Defining/specifying the future system state according to the identified factors
